Solid phase
- Official name
- Magnesium(II) sulfate hydrates
- Secondary names
- Magnesium sulphate hydrates
- Family
- ionic solid
- Class
- normal salt
- Compound type
- sulfate
- Comments
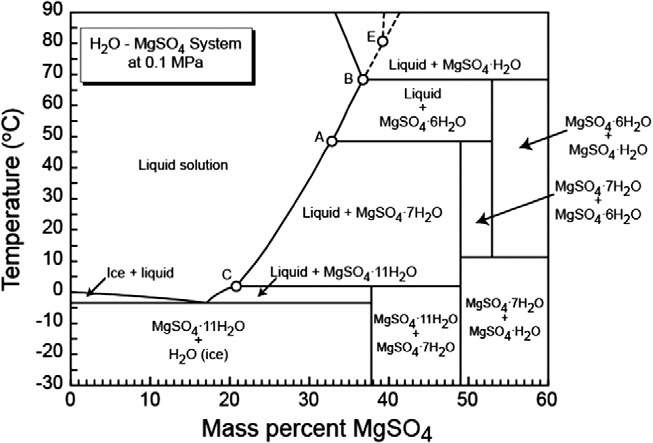
- Magnesium sulfate hydrates occurs as minerals: Kieserite (monohydrate), Starkeyite (tetrahydrate), Pentahydrite (pentahydrate), Hexahydrite (hexahydrate), Epsomite (heptahydrate) and Meridianite (undecahydrate).
- Formula
- $Mg^{2+} \cdot SO_4^{2-} \bullet nH_2O$
- Chemical formula
- MgSO4•nH2O
- Elemental formula
- (Mg2+) S (O)3-13 (O-)2 (H)2-22
- Isotope mixture type
- terrestrial abundance
16.0
- Composition comments
- the is a dozen of different hydrates with hydration number between 1 and 11
- Class
- normal salts (07)
- Type
- hydrated simple normal salts (07.04)
- Phase type
- crystalline
- Crystal system
- various
- Crystal class
- various
- Crystal class symbol
- various
- Crystal spacegroup
- various
- Comments
- The structure depends on degree of hydration
- Molar mass
- 138.38 (n=1) - 336.545 (n=11) $g/mol$
- Density
- 2.445 (n=1) - 1.512 (n=11) $g/cm^3$
- State NTP
- solid
- Refringence type
- various
- Pure color
- colorless
- Color
- colorless
- Diaphaneity
- transparent to translucent
- Luster
- vitreous